More Patients, Less Time from Angelica F. Dizon
$199.00 $59.00

More Patients, Less Time Crucial Assessment Techniques, Pathophysiology Unveiled from Angelica F. Dizon
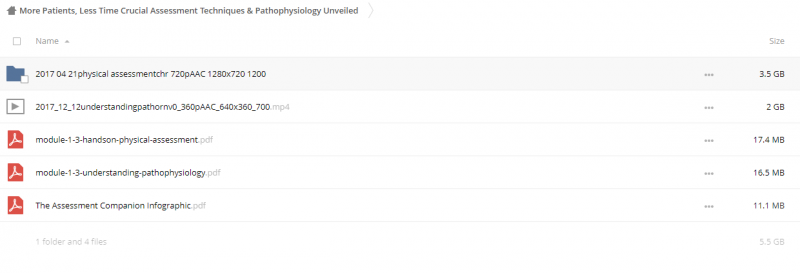
Archive : More Patients, Less Time from Angelica F. Dizon
Get More Patients, Less Time from Angelica F. Dizon on Salaedu.com
Are you missing vital clues in your physical assessments?
In today’s clinical world, healthcare professionals are tasked with seeing more patients in less time… making it more important than ever that you conduct quick, yet precise head-to-toe assessments.
With this cutting-edge online course, you’ll get step-by-step guidance on how to quickly and thoroughly assess patients, understand the pathophysiology behind their condition, intervene effectively, and proper techniques to documenting your assessments and findings.
In 6 self-paced modules, you will be able to predict a differential diagnosis by identifying cardiac, respiratory and neurological disorders!
Walk away with advanced knowledge to:
- Interpret pathophysiology and differential diagnoses for crackles, wheezes, rhonchi and rubs
- Discuss management of obstructive vs. restrictive lung disease
- Practice a thorough 6-part neurological exam and document findings
- Distinguish whether abnormal S1 and S2 heart sounds are pathological or benign
- Outline an effective method to review options in pharmacologic therapy for any condition
- And so much more!
Improve your confidence, increase efficiency, and eliminate errors today!
Learn tips, tricks, and tools to conduct a quick and precise head-to-toe assessment.
- Assess the patient using the most comprehensive approach
- Evaluate baseline and identify patient status changes
- Devise tips and tools to perform a more efficient exam without missing key clues
- Conduct proper assessment skills – inspection, palpation, percussions, auscultation
Knowing the different murmurs, their presentation, sounds and location to accurately pinpoint the disease process.
- Examination of mitral, tricuspid, pulmonary, and aortic
- Auscultation sites, sequencing and skills
- Characteristics of a functional murmur
- 7-point classification
- When does a murmur become pathologic?
- Strategies for detection of abnormal cardiac sounds
- First-hand partner demos: Practice and learn with examples
Identifying the different breath sounds and their locations to narrow down diagnosis
- Physical assessment of the respiratory system – key points of normal anatomy to remember
- Identification of normal, abnormal, decreased or absent breath and lung sounds
- Assessment and techniques of Tactile Fremitus, percussion, lung auscultation
- Interpreting what you are hearing and what you should expect to hear:
- Bronchial, Broncho-vesicular, Vesicular Breath Sounds
- Bronchophony, Egophony, Whispered Pectoriloquy
- Death Rattle, Absent Breath Sounds
- Learning the adventitious sounds like Crackles, Rhonchi, Stridor, Wheezes and what to do with them
- What Lung Sounds to expect in different disease states
- First-hand partner demos: Practice with sounds — listen, assess, and learn
Mastering the 6-part components of a Neuro exam in less time.
- Unraveling the 6-Part components of a thorough Neurological Examination
- ABCT Components of Mental Status
- Key points and clues of using Confusion Assessment Method (CAM) Instrument and what can be diagnosed as a result
- Evaluate an efficient and accurate assessment of normal vs. abnormal findings for: altered mental status, cranial nerves, motor, sensory, cerebellar functions, reflexes
- Danger Signs for abnormal findings and how to identify diseases by physical examination
- First-hand partner demos: Practice with case studies and proper assessment
- Key clues you can’t miss
- Risk factors, readings, subjective and objective data
- Plan of care
Get More Patients, Less Time from Angelica F. Dizon on Salaedu.com
Endocrine and Metabolic Problems
- Pituitary disorders
- Hypoglycemia
- Free radicals — essential in health, deadly in disease
- Diabetic ketoacidosis
- Apoptosis
- Adrenal gland dysfunction
- Addison’s disease
- Jaundice
- Implications of hormones
- Thyroid disorders – mechanism of onset affects treatment
Cardiovascular and Renal Problems
- Starling’s Law – normal capillary flow
- Heart failure
- Relationship between cardiac diseases and hypertension
- Unraveling hypertension
- Current concept on cardiogenic shock
- Atherosclerosis – the role of inflammation
- Anaphylaxis
- Acid-base disorders
Respiratory Problems
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease exacerbations
- Obstructive lung diseases affecting the mechanics of lung ventilation
- Sudden death in asthma
- Acute lung failure/ARDS
- Arterial blood gases made simple
Shock
- Common mechanisms of all types of shock
- The cardinal role of mediators in shock
- Newer therapies based on current pathophysiological understanding
- End points of resuscitation
- What type of shock is this?
The Immune System
- Inflammation – acute phase response
- Systemic inflammatory response
- Infection – part of a bigger picture
- Multiple organ dysfunction syndrome
- Stress reaction
- Autoimmune diseases
Angelica F. Dizon, MD, BSN, MBA-HCM, RN, is a registered nurse and a Doctor of Medicine with two decades of experience in clinical practice and academic teaching, predominantly in the hospital setting.
Angelica has been well recognized for her past work in medical surgical roles, and has also gained experiences working in home health care and skilled nursing. Most recently, she’s serving as the director of clinical services in one of the leading home healthcare agencies in Maryland.
Her diverse experiences have provided her with a unique patient perspective to facilitate the highest level of patient care – anticipated findings, as well as identification and monitoring of various disease states. Her passion and talent for educating and mentoring other healthcare professionals will make this an event you don’t want to miss!
Health and Medical course
More information about Medical:
Medicine is the science and practice of establishing the diagnosis, prognosis, treatment, and prevention of disease.
Medicine encompasses a variety of health care practices evolved to maintain and restore health by the prevention and treatment of illness.
Contemporary medicine applies biomedical sciences, biomedical research, genetics, and medical technology to diagnose, treat, and prevent injury and disease,
typically through pharmaceuticals or surgery, but also through therapies as diverse as psychotherapy, external splints and traction, medical devices, biologics, and ionizing radiation, amongst others.
Medicine has been around for thousands of years, during most of which it was an art (an area of skill and knowledge) frequently having connections to the religious and
philosophical beliefs of local culture. For example, a medicine man would apply herbs and say prayers for healing, or an ancient philosopher and physician would apply bloodletting according to the theories of humorism.
In recent centuries, since the advent of modern science, most medicine has become a combination of art and science (both basic and applied, under the umbrella of medical science).
While stitching technique for sutures is an art learned through practice, the knowledge of what happens at the cellular and molecular level in the tissues being stitched arises through science.
More Course: FITNESS – HEALTH – MEDICAL
Outstanding Course: Bob Proctor – Living the Legacy
1 review for More Patients, Less Time from Angelica F. Dizon
Add a review Cancel reply
Related products
HEALTH - FITNESS - LIFESTYLE - MEDICAL
HEALTH - FITNESS - LIFESTYLE - MEDICAL
HEALTH - FITNESS - LIFESTYLE - MEDICAL
Somatic Interventions for Treating Complex Trauma with Janina Fisher, Ph.D. from Janina Fisher
HEALTH - FITNESS - LIFESTYLE - MEDICAL
HEALTH - FITNESS - LIFESTYLE - MEDICAL
HEALTH - FITNESS - LIFESTYLE - MEDICAL
HEALTH - FITNESS - LIFESTYLE - MEDICAL
Fast Confidence [How To Be More Confident │Confidence Building] from Sharon Melnick, Ph.D.
HEALTH - FITNESS - LIFESTYLE - MEDICAL
Fitness Mentors – Audio Lectures, Practice Tests and Study Guide for the NASM CPT Ex








![Fast Confidence [How To Be More Confident │Confidence Building] from Sharon Melnick, Ph.D.](https://tradersoffer.forex/wp-content/uploads/2017/05/Sharon-Melnick-Ph.D.-Fast-Confidence-How-To-Be-More-Confident-│Confidence-Building-220x261.png)

king –
“We encourage customers to contact Customer Service and think twice before making payment. All course contents will be similar to what is from the author.”
Thank you!